First Aid Kits
First aid kits are an essential item for every workplace be that in an office, factory or building site they are a legal requirement. Employers have a duty of care towards their employees as well as contractors and visitors to the site. Sufficient first aid supplies must be provided within the workplace to meet requirements of your specific workplace.
At Scully First Aid Supplies all our workplace first aid kits comply to HSA regulations. Each kit comes complete with high quality first aid supplies to treat a range of common workplace injuries. We have available a range kits available to choose in order to match your requirements. These include a range of cases for rigid plastic cases to soft nylon bags to wall mountable first aid points.
To see our wide range of first aid kits click here First Aid Kits and Bags
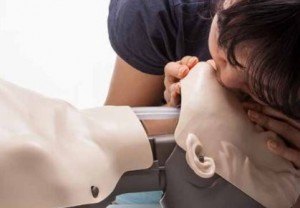
First Manikin to Help You Visualize the Effects of CPR
A manikin has been invented that helps first responder trainees visualize the effects of CPR.
First aid has been taught by organizations like St. John’s Ambulance and The Irish Red Cross for over a century, saving countless lives in warfare, community events and everyday life. The practice of first aid is always updating as new technology and safer procedures are brought in with the aim of saving even more lives.
Now with the unveiling of the Brayden Illuminating CPR Manikin, learning first aid has never been more engaging. A normal CPR manikin offers excellent experience and practice for when a first responder needs to put their practice into action, but the Brayden Illuminating Manikin let’s the first aider and trainees see what exactly their actions are doing to the manikin’s body by lighting up the circulation of blood around the body and signalling the quality of the CPR and chest compressions.
First of its Kind
The Illuminating Manikin is the first of its kind, and has been built to build the confidence of trainee first aiders, whilst offering them improved understanding of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and aiding them in the retention of that knowledge. 3 interrelated sets of LED lights give the trainee real time feedback of their CPR performance & function.
Chest Compression
The chest compression lights represent how much blood is being circulated around the body by the person administering the treatment. The chest compression light only fully illuminates when the depth of compressions is over 5cm.
Blood Circulation
The manikin has lights that represent the flow of blood from the heart to brain. The speed will vary with the depth and speed of compression being administered. The light will only fully illuminate once the rate of compressions matches the recommended amount, which is 100 per minute.
Quality of CPR Light
The quality light illuminates to represent that blood is reaching the brain. The quality light only illuminates if all factors are correct, in order to illuminate the quality light, the depth and speed of compressions need to be precise.
A set of 6 alkaline batteries will give Brayden the power to perform 160,000, giving the manikin plenty of uses before they need changing, or the manikin can be powered with an AC adapter.
To find out more about or range of manikins and our training aids click on the link Training Aids
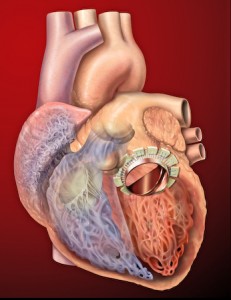
Exciting Leap Forward in Cardiovascular Science – Heart Muscle Cells Regrown
Scientists have discovered a way to stimulate heart muscles to grow again, which could make the recovery of heart attack patients much easier.
In a joint project between the Weismann Institute of Science in Israel and the Victor Chang Institute in Australia, scientists have found a way of stimulating heart muscle cells to grow in mice.
Human heart cells find it difficult to heal after cardiac arrest, which means that recovery is often a long and arduous journey. Blood, skin and hair cells can all regrow, but after the first week of birth human heart cells stop dividing. Conversely salamanders and fish are able to regenerate their heart muscles automatically.
“The dream is that one day we will be able to regenerate damaged heart tissue, much like a salamander can regrow a new limb if it is bitten off by a predator,” said Richard Harvey of Sydney’s Victor Chang Institute.
“There’s always been an intense interest in the mechanism salamanders and fish use that makes them capable of heart regeneration. There are various theories why the human heart cannot do that, one being that our more sophisticated immune system has come at a cost.”
The scientists have been able to make the heart cells in a mouse regenerate by stimulating a signalling system in their heart. Using the hormone neuregulin mice heart cells divide incredibly.
Neuregulin stops being produced in humans 1 week after birth, that’s why the heart cells stop dividing, in mice it can be around 20 weeks.
Approximately 10,000 people die each year from cardiovascular disease in Ireland
Approximately 10,000 people die each year from cardiovascular disease (CVD) – including coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke and other circulatory diseases. CVD is the most common cause of death in Ireland, accounting for 33% of all deaths. As obesity and sedentary lifestyles, both large contributors to heart disease, become more prevalent, this leap in medical science could be a way of battling the disease, though Harvey predicted it would take around 5 years before scientists were ready to test on humans.
The best way to prevent heart disease in your life is simple, be active for at least half an hour everyday, eat a balanced diet that is low in fat and salt and avoid over drinking alcohol and smoking altogether.
Scully First Aid Supplies are a distributor of defibrillators and other bespoke medical equipment, to see more visit our site https://www.scullyfirstaidsupplies.ie/
AED Finder & Emergency Responder App
Ever wondered where your local defibrillator is? Wonder now more, the AED Finder & Emergency Responder App is here. Download it for Android or Iphones phones for free!!
It is hugely important in today’s society that each workplace, school, college, village, town, city, sports club etc…has a defibrillator. This app allows people to locate their nearest defibrillator and also brings them through the steps in the event of an emergency.
If you are interested in purchasing a defibrillator please call us today and we will be happy to talk you through or wide range of defibrillators and AED Cabinets.
Click on this link to see our range of defibrillators https://www.scullyfirstaidsupplies.ie/
Well done to the folks at http://findmydefib.com/ for a fantastic app and if your defibrillator isn’t registered on this app then do, you could save a life.
First Aid for Burns
The information contained within this article will assist you in identifying the cause, severity and percentage of a burn. It is important that you do not attempt to treat a burn until you are certain any potential hazards have been neutralized.
1) Classification for Burns
Superficial
1. Reddening and discolouration of the skin
2. Some swelling
3. Pain
Partial thickness
1. A combination of discolouration, swelling and blistering of the skin
2. If any blisters have burst a clear watery fluid from the site (Serum)
3. May involve one or more blisters being formed
4. Pain
Full thickness
1. Pitted/charred appearance
2. Surrounding skin around burn site may appear wax-like and false
3. Clear watery fluid may leak directly from the burn site
4. Blisters may form around the site of the main charred area but not on it
5. If the skin is badly charred, the casualty may not experience pain as the nerve endings may be destroyed
2) Treatment of burns
1. Ensure that the cause of the burn does not endanger your life or that of the casualty
2. Assess that the casualty is still conscious (if they are not, carry out the ABC of resuscitation)
3. Establish the cause of the burn – if a chemical is suspected go to section 4
4. Immediately begin to cool the burn. Continue cooling under water for 10 minutes.
NB – DO NOT over cool, you may lower the body temperature too much.
5. If the burn has affected a limb e.g. arm, remove any constrictive items such as watches, rings etc., in anticipation of any swelling.
NB – DO NOT remove if directly in contact with the burn.
6. Initially cool under running water for 10 minutes or until burning sensation has stopped and then apply a non adhesive sterile dressing.
3) Dressing a Burn
1. When a burn has been cooled sufficiently a sterile non fluffy dressing should be applied.
2. Gently remove any rings, watches, belts, shoes or smouldering clothes from the injured area before it begins to swell.
NB – If Clothing is burnt onto the wound DO NOT pull off.
3. A water based gel soaked sterile dressing is ideal as it helps prevent burn-progression and infection.
4. If a suitable dressing is not available, you may improvise using a sterile triangular bandage or cling film.
DO NOT apply any dressings that may cause a tourniquet effect.
4) Clothing on Fire
If a casualty’s clothing is on fire the greatest danger will be to their airway. Due to a combination of panic and pain they may be on their feet and moving flames will naturally rise and endanger the airway of the casualty.
Action to take
1. Initiate the fire alarm.
2. Attempt to get the casualty flat on the floor – you may have to physically push them over using using a broom or fire blanket, etc. to ensure you do not get exposed to the flames.
3. Once the casualty is flat on the floor try to smoother the flames. Ideally use a fire blanket or improvise with a woolen or cotton blanket.
4. Ensure the casualty’s Airway, Breathing and Circulation are present.
5. Cool the burn(s).
NB – DO NOT over cool, you may lower the body temperature too much. DO NOT roll the casualty. Extinguish from the head down.
5) Complicated burns
Airway
All burns involving the airway are potentially life threatening. Attempt to treat any external burns and dial 999/112 for help.
Burns to the respiratory system
As well as sustaining a damaged airway, the lungs and associated tissue may be damaged by hot fumes and smoke. This may cause blistering to the tissue and requires urgent medical attention.
Circulation
Normally resulting from chemical contamination, a circle burn involves damage to the skin that encircles any part of the body such as the arm. As it swells it constricts circulation of other body systems. Treat as in section 3 and dial 999/112 for help.
6) Burn severity
The severity of burns depends on the area of the body affected and the extent i.e. Partial thickness or Full thickness.
1% OF THE BODY’S SURFACE IS ROUGHLY EQUIVALENT TO THE PALM OF THE CASUALTY’S HAND. CASUALTIES SHOULD BE REFERRED TO HOSPITAL IN THE FOLLOWING CIRCUMSTANCES:
- Any Superficial burn covering more than 5% of the body’s surface.
- Any Partial thickness burn covering more than 1% of the body’s surface.
- Any Full thickness burns. Any burns involving children.
- All burns involving feet, hands, face or genital areas.
- All burns that extend around a limb.
- Any burns with a mixed pattern of depth.
- If unsure of depth or severity of burn.
For a full range of Burn Care products visit https://www.scullyfirstaidsupplies.ie/types/burn-care/
External Bleeding Tips
Caring for Diabetic Feet – Chiropodists
If a patient is suffering with diabetes, foot care is vital. They tend to heal more slowly from cuts, sores and wounds, because the body’s processes that resist infection are more lethargic. So people with diabetes have to take extra care with their feet because if they get infected they may have to have their feet amputated.
It is often the case that diabetics, and also elderly people, have poor circulation, which makes healing of wounds and infection much slower. Those with poor circulation will know that it affects the areas furthest from the heart, such as the feet. Diabetes can also do damage to nerves in patient’s feet and give them stiff joints.
It is the job of a chiropodist to keep diabetes patient’s feet in good working and healthy order. If you have diabetes, you should get in touch with your local chiropodist to look after the care of any foot problems you may have.
Chiropodists can help you look after things like:
- Corns
- Calluses
- In-grown toe nails
- and much more
It is paramount that you don’t try to take care for your own diabetes feet issues. You might make things worse and put yourself in an even worse situation.
Things you can do to keep maintain healthy feet:
- Wash them daily in lukewarm water, using a weak soap, and dry them thoroughly, not forgetting in between your toes.
- Thoroughly check your feet, every day or get someone you live with to do it for you. If you or they find any cuts, sores, bruises, toenail colour changes you should call your chiropodist for an appointment.
- Have the chiropodist come round for regular appointments, you may need professional help every few months if your circulation is very bad.
- Ventilate your feet as often as you can, if you are sat down, take your shoes and socks off. Though if you are going around the house, wear some sandals or slippers to prevent yourself from getting them cut or infected.
- You would be surprised to find out that proper diabetes foot care could not only save your feet, it could even save your life.
If you are a diabetes sufferer why not look at our blood glucose meters in our diabetes section by clicking on this link.
Wearable Pain Relief Technology
NeuroMetrix, an American company have created a piece of wearable technology that offers its user pain relief, if it’s a success we might see it widely used in Ireland.
Quell, attaches to your calf and releases electrode driven non-invasive nerve stimulation to relieve the wearer of chronic pains. NeuroMetrix promise that the Quell wearer will get relief from their aches and pains within 15 minutes and can provide 40 hours of pain relief on a single charge.
The clever strap can also monitor your quality of sleep, and provide you with information via a clever IOS app that connects to Quell via bluetooth.
“It works by stimulating the sensory nerves in your calf, then sends neural pulses to your brain, where they trigger the body’s natural pain relief response releasing endogenous opioids. Finally, these opioids send pain signals toward the delta opioid receptor, which is what triggers those tedious feelings, and reduces the amount of pain you’re experiencing.” – Source Engadget
It’s been approved by the American FDA and already featured in a gadgetry exhibition this year called, the Consumer Electronics Show.
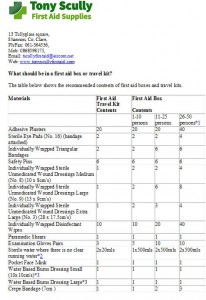
What should be in your workplace first aid kit?
Here at Tony Scully First Aid Supplies we are always asked, what should be in our workplace first aid box.
Below are the details to make sure your company is Health & Safety Authority compliant.
Notes
*1: Where more than 50 persons are employed, pro-rata provision should be made.
*2: Where mains tap water is not readily available for eye irrigation, sterile water or sterile normal saline (0.9%) in sealed disposable containers should be provided. Each container should hold at least 20ml and should be discarded once the seal is broken. Eye bath/eye cups/refillable containers should not be used for eye irrigation due to risk of cross infection. The container should be CE marked.
*3: Where mains tap water is not readily available for cooling burnt area.
Is there some flexibility on the contents of boxes and kits?
The above Table provides a general guide on the recommended contents of occupational first aid boxes and kits based on numbers employed. Quantities indicated in the Table are minimum numbers and can be increased. The requirements for sterile water and water based burns dressings as per note 2 and 3 above are only where there is not a wholesome supply of tap water available. Also a single paramedic shears and pocket face mask is considered adequate.
Occasionally the quantities indicated in the Table will be insufficient and the actual amounts required should be based on a risk assessment. An obvious example is that drivers of dangerous goods vehicles would require a quantity of 2x 500mls of sterile water for eye irrigation in their travel kits due to the risk of contact with hazardous chemicals.
If you need a new First Aid Box or the contents of your box replenished please contact us and we will help you out.
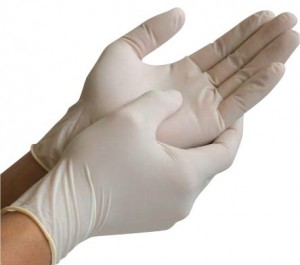
10 Things You’ve Always Wanted to Know About Powder Free Latex Gloves but Never Thought to Ask.
Medical gloves first appeared in the medical industry in 1889, but only came into common use as AIDS became widespread in the 1980s. It’s strange to think how commonly they are used today, though it took nearly a century to get to that point.
Gloves are a necessary part of the medical profession, so Tony Scully First Aid Supplies decided to honour their simple but vital role with an article that explores their history, creation and uses.
The First Sterile Medical Gloves
William Stewart Halsted M.D was the first to use sterile medical gloves while he was working at Johns Hopkins University, in America. Germ theory had recently been introduced and Halsted was using carbolic acid to create a sterile environment and wash his and his nurse’s hands. The acid was damaging to the skin on one of his nurse’s hands, so Halsted looked to the Goodyear Tyre & Rubber Company and asked if they could make a glove that could be sterilised in carbolic acid while being dextrous enough to perform clear tasks.
The First Disposable Sterile Medical Glove
Ansell, an Australian company were the first to create a disposable glove, allowing medical professionals to deal with the less glamorous sides of their jobs in a hygienic fashion, whether that be dentist’s fingers in mouths, to dealing with human excrement. Ansell actually based their production techniques for making medical gloves on how condoms were made.
Criminals Using Medical Gloves
Medical gloves used to be popular with criminals as they wore them to commit crimes. Their thin second skin like material and tight fit offer a high dexterity in order to perform tricky actions, but this is also their downfall as the thin latex can actually allow fingerprints to pass through them.
Double Gloving
Putting two sets of gloves on is known as double gloving. Wearing two layers of medical gloves will offer you significantly more protection against any perforation in comparison to using just one glove.
Don’t Use Oils
Oils will breakdown the glove and could cause perforation, only use water-based hand lotion and dentists should discourage their patients from wearing oil based lip balm.
Ensure Alcohol is Dry
If you are using an alcohol based hand gel allow it to become absolutely dry or the alcohol may breakdown the glove and cause a perforation.
Don’t Wear Rings or Jewellery Under Medical Gloves
Don’t wear rings or jewellery under your gloves, they will rub on the inside of the glove and likely pierce them. Rings and jewellery can also harbour bacteria and viruses. This is the same for artificial nails, they will likely break the gloves and could be unclean also.
Medical Gloves Have an Expiry Date
You may not have known that medical gloves actually have an expiry date. You should rotate your gloves so the oldest are used before the newest. They need to be kept in a cool, dark and dry place, well away from air conditioners and x-ray machines. Don’t remove them from the box they came in so they can be easily identified.
Never Wash Your Disposable Gloves
Medical gloves should only be used once, washing them will cause them to breakdown from the moisture. Instead wash your hands and then thoroughly dry them. Moisture and heat inside the gloves will harbour bacteria. It is best to have clean and dry hands to prevent any spread of bacteria.
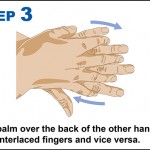
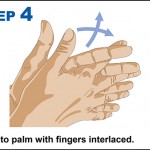
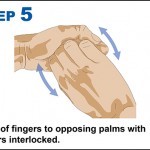
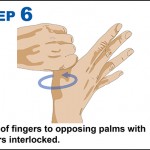
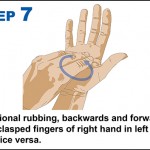
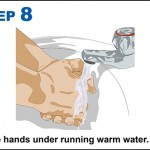
10 steps to improving hand hygiene
Certain bacteria can remain active on our hands for up to three hours. During this time bacteria can spread to everything we touch.
Why is hand hygiene so important?
- Millions of germs are picked up by hands during every-day activities. Many of these are harmless but some cause illness such as colds, flu and stomach bugs.
- Hand hygiene is essential to prevent the transfer of these germs to other people and surfaces to stop the spread of illness.
- Poor hand hygiene can lead to the spread of Campylobacter, Salmonella, MRSA, Impetigo and Flu.
The information contained is for guidance only and should not be used as a substitute for recognized training.
Protect your workforce!!
Check out of Hygiene section and purchase antibacterial hand wash or hand sanitizer for your workplace.
Defibrillator Drones: Ambulances of the Future
In Ireland it has been predicted that one day defibrillators will be as common as road signs. The day is still yet to come, though they are becoming more widespread in schools, sports centres and airports. Now a new portable defibrillator idea has been developed into reality, the defibrillator drone.

Alec Momont, a graduate of industrial design at TU Delft university in Holland, has invented the Ambulance Drone, which can travel at 100km/h and has a built in defibrillator. The Ambulance Drone has propellers that fold away and a handle so that it can conveniently be lifted once it lands.
Momont says that the Ambulance Drone can increase survival after cardiac arrest from 8% to 80%. The drone’s quick speed and its advantage of avoiding traffic and winding road networks means it can get to an emergency scene 10 times quicker than an ambulance. Time is crucial during cardiac arrest and this speedy outreach time could save tens of thousands of people in the UK alone eery year.
The drone has a camera, microphone and speaker fitted so the remote paramedic that flies the drone can give the emergency caller calm and safe instructions on how to use it. The defibrillator pads are kept in the drone’s nose and each pad is clearly labeled so there is no confusion when an emergency arises.
There is a promotional video of the drone in action below, it shows an older man suffering a cardiac arrest in a public venue and a young woman calling an ambulance. A clock starts to count after she has dialed, and the paramedic on the phone tells her that he is sending a drone. She rushes outside and in under a minute the drone appears. With cool and calm instructions, the woman places the pads correctly and the paramedic then remotely administers the shock. Within 2 minutes the man is saved and everyone has a hug because the old fella is up and alive.
Here at Tony Scully First Aid Supplies we would be shocked if ambulance drones didn’t start to appear in the not too distant future. The technology is incredible and has the chance to save so many lives. For now all we can hope is that defibrillators keep being put in as many public places as possible.
For more information on Defibrillators check out our full range on our site.
Have I got Diabetes?
In the absence of a register of people who have diabetes no-one can be entirely sure how many people In Ireland live with diabetes; the Institute of Public Health’s report Making Diabetes Count (2007) estimated that there were about 143,000 people with diabetes in Ireland (based on in 2005 figures) and predicted that this number would increase by 37%, to 194,000 people, by 2015.
To help spread the word we’ve put together some information on what diabetes is, the symptoms you will notice and what you’ll need once you’ve been diagnosed.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition which effects the amount of glucose (a source of energy from food) in the body, rendering it too high for the body to use it.
This happens because the pancreas is unable to produce any, or enough insulin to help open the body’s cells. Also, the body may produce insulin, but the insulin produced may not work in the correct manner, which is known as insulin resistance. Insulin is vital to keep the body living.
Without insulin, glucose builds up in the blood and is unusable as food.
There are two types of diabetes:
Type 1 – The body is unable to produce its own insulin.
Type 2 – The body can create insulin but it isn’t working correctly.
What are the Symptoms?
The body reacts to the build up of Glucose in the system by attempting to flush the excess out of the body in urine.
While Type 1 Diabetes signs and symptoms are very obvious, Type 2 may not be noticed until a routine medical check has been done.
The main symptoms to check for include:
Passing urine more often, especially in the night
– Feeling more thirsty
– Extreme Fatigue
– Unexplained weight loss
– Itchy genitals or thrush
– Healing is slower when cut
– Blurry vision
If you are worried you have these symptoms go and see a doctor as soon as possible.
If I’m Diagnosed with Diabetes What can I do?
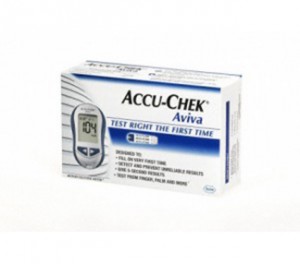
Diabetes is a life long health condition. Once you are diagnosed, you will need to change your diet to become diabetes friendly and get a glucose meter to check your blood glucose levels.
To manage diabetes successfully you’ll need a meter. Here at Tony Scully First Aid Supplies we supply the ACCU-CHEK® Aviva Blood Glucose Meter. The Accu-Chek Aviva is easy to operate and as there is no set-up required and no coding, it comes ready to use straight out of the box. This enables the user to begin testing easily and quickly.
Check out our Diabetes Monitoring & Testing section on our site https://www.scullyfirstaidsupplies.ie/types/diabetes-monitoring-testing/